Vaccination has revolutionised control of infectious disease in our pets. It is essential that all pets are adequately vaccinated to help protect the pet population as a whole. Responsible pet care requires puppies to be given their initial course of vaccinations, but this cannot protect them for the rest of their lives. Adult dogs require regular vaccination to maintain immunity against disease
Please give us a call to discuss a suitable vaccination regime for your pet puppy or dog.
![]()
Puppy Vaccination
Puppies are temporarily protected against many diseases by antibodies received through their mother’s milk. These maternal antibodies decline in the first few weeks of their lives, after which they need a vaccination to induce immunity. The age at which maternal antibodies drop enough to require vaccination is highly variable, which is why a series of vaccinations is necessary in a puppy.
![]()
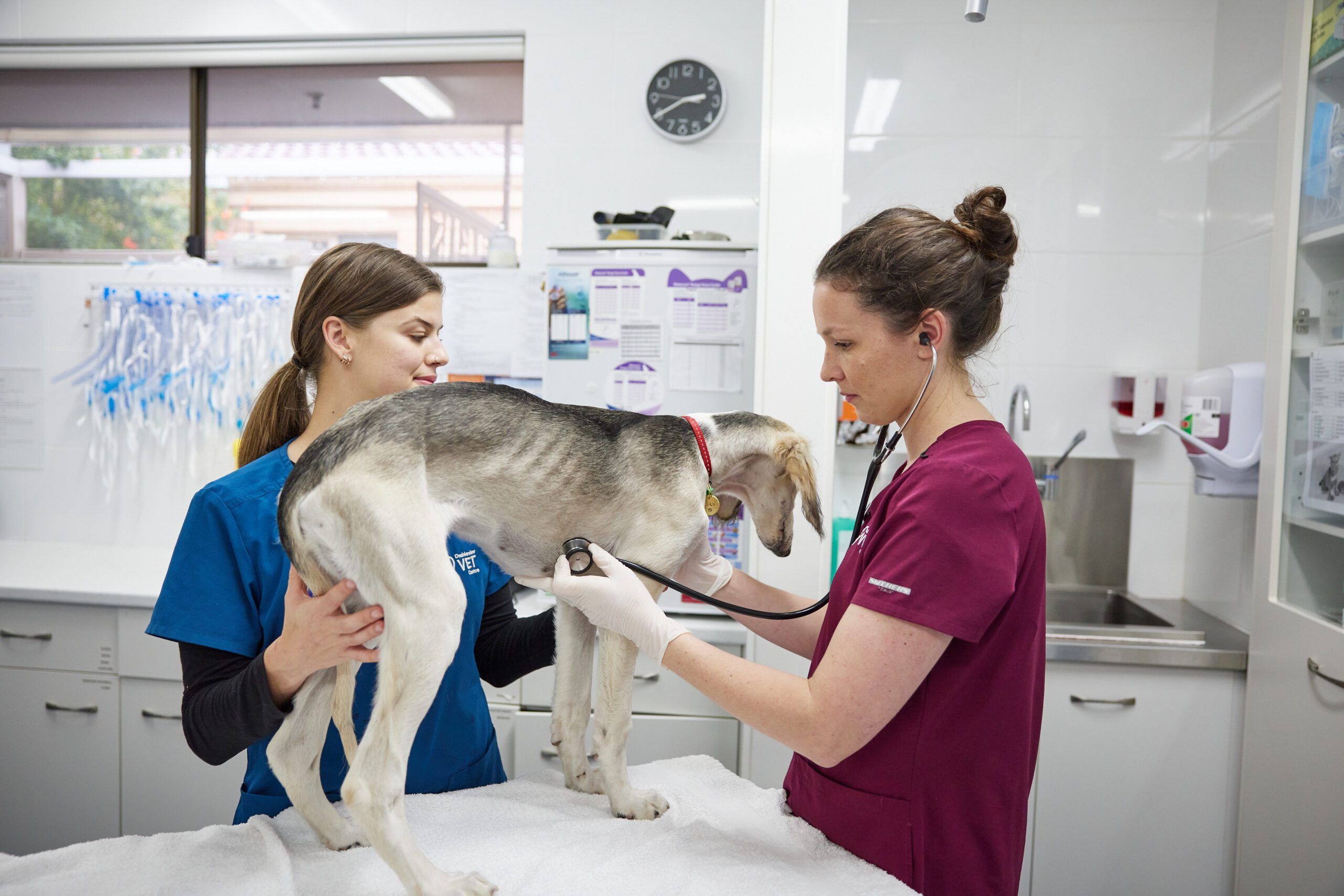
Adult Dog Vaccination
The immunity from puppy vaccination weakens over time and your pet can again become susceptible to disease. Annual health checks and booster vaccinations, as required, will provide the best protection for the life of your pet.
![]()
After Vaccination Care
Following vaccination your dog may be off-colour for a day or two, or have some slight swelling or tenderness at the injection site. Access to food and water and a comfortable area to rest are usually all that is required for a quick recovery. However, if the response seems more severe, you should contact us for advice.

Canine Parvovirus
Canine parvovirus is a disease that affects dogs of all ages but is most serious in young pups and older dogs. The virus attacks the intestines causing bloodstained diarrhoea, uncontrollable vomiting and severe abdominal pain. Some infected dogs will die from parvovirus, even if they receiveintensive veterinary care.
Parvovirus is spread via dog faeces and is very persistent in the environment even after the faeces has been cleaned away. For this reason, it is not necessary to have direct contact with other dogs for the disease to be spread. The virus is so persistent that an infected dog’s environment needs to be cleaned with a potent disinfectant to prevent spread to other dogs. Outbreaks occur regularly especially in summer, with an estimated 20,000 dogs infected every year in Australia.
Canine Distemper
Canine distemper is a highly contagious viral disease that can affect dogs of any age with young puppies being at highest risk.
Symptoms vary but can include fever, coughing, sneezing, nasal discharge, vomiting, diarrhoea, loss of appetite and depression. Muscle tremors, fits and paralysis usually occur later in the disease. Treatment is usually ineffective and the recovery rate very low. Dogs that do recover may have permanent brain damage.
Canine Infectious Hepatitis (also known as Canine Adenovirus type1)
Canine infectious hepatitis is a viral disease which, like distemper is extremely contagious and often fatal. Dogs of any age can become infected, however severe cases are rare in dogs over two years of age.
Symptoms include high fever, depression, loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhoea and acute abdominal pain. In severe cases death can occur within 24 to 36 hours. Dogs that recover may develop long-term liver and kidney problems and can act as carriers spreading the disease to other dogs for many months.
Canine Cough
Canine cough is a condition produced by several highly infectious diseases, which can be easily spread wherever dogs congregate, such as parks, grooming salons, doggy day care, shows, obedience schools and boarding kennels. Among the infectious agents associated with canine cough is the bacterium known as Bordetella bronchiseptica and the canine viruses parainfluenza, adenovirus type 2 and distemper.
Affected dogs have a dry hacking cough which can persist for several weeks. It is distressing for pet dogs and their owners. It is a major problem for working and sporting dogs. Pneumonia can also be a consequence of infection.
